青海省6种高寒禾本科牧草的耐盐性
English
-
参考文献
[1] VEERANAGAMALLAIAH G, CHANDRAOBULREDDY P, JYOTHSNAKUMARI G, SUDHAKAR C. Glutamine synthetase expression and pyrrotine-5-carboxylate reductase activity influence proline accumulation in two cultivars of foxtail millet (Setaria italica L. ) with differential salt sensitivity. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2007, 60: 239-244. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2006.10.012
[2] BARTELS D, SUNKAR R. Drought and salt tolerance in plants. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 2005, 24: 23-58. doi: 10.1080/07352680590910410
[3] 乔枫, 罗桂花, 耿贵工. 蚕豆幼苗对NaCI和NaHCO3胁迫的生理响应. 安徽农业大学学报, 2011, 38(5): 783-787. QIAO F, LUO G H, GEN G G. Physiological responses of vicia faba seedlings to NaCl and NaHCO3 stress. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2011, 38(5): 783-787.
[4] MELONI D A, OLIVA M A, MARTINEZ C A. Photosynthesis and activity of superoxide dismutase, peroxidese and glutathione reductase in cotton under salt stress. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2003, 49: 69-76. doi: 10.1016/S0098-8472(02)00058-8
[5] 陈惠哲, NATALIA LADATKO, 朱德峰, 林贤青, 张玉屏, 孙宗修. 盐胁迫下水稻苗期Na+和K+吸收与分配规律的初步研究. 植物生态学报, 2007, 31(5): 937-945. CHEN H Z, NATALIA L, ZHU D F, LIN X Q, ZHANG Y P, SUN Z X. Absorption and diatribution of Na+ and K+ in rice seedline under salt stress. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2007, 31(5): 937-945.
[6] 乔旭, 黄爱军, 褚贵新. 植物对盐分胁迫的响应及其耐盐机理研究进展. 新疆农业科学, 2011, 48(11): 2089-2094. doi: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2011.11.023 QIAO X, HUANG A J, CHU G X. Research progress in the effects of salt stress on plant and the mechanism of plant resistance. Agriculture Science of Xinjiang, 2011, 48(11): 2089-2094. doi: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2011.11.023
[7] 沈艳, 谢应忠. 牧草抗旱性和耐盐性研究进展. 宁夏农学院学报, 2004, 25(1): 65-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0747.2004.01.019 SHEN Y, XIE Y Z. The progress of studies on forage grass drought resistance and salt tolerance. Journal of Ningxia Agricultural College, 2004, 25(1): 65-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0747.2004.01.019
[8] 余玲, 王彦荣, 孙建华. 野大麦种子萌发条件及抗逆性研究. 草业学报, 1999, 8(1): 50-57. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-5759.1999.01.008 YU L, WANG Y R, SUN J H. Studies on germination condition and stress resistance of Hordeum brevisubulatum seeds. Journal of Grass Industry, 1999, 8(1): 50-57. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-5759.1999.01.008
[9] 毛培春, 王勇. 不同禾本科牧草材料种子萌发的耐盐性试验. 内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2004(2): 115-118. MAO P C, WANG Y. Experiment on salt resistance in seed germination stage of six grass varieties. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2004(2): 115-118.
[10] 王晓龙, 李红, 闫利军, 米福贵, 于洁, 贾振宇, 杨曌, 杨伟光. 5种禾本科牧草种子萌发及幼苗耐盐性鉴定. 种子, 2016(8): 27-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2690.2016.08.022 WANG X L, LI H, YAN L J, MI F G, YU J, JIA Z Y, YANG Z, YANG W G. Salt-tolerance of seed germination and seedling growth for five grass species. Seeds, 2016(8): 27-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2690.2016.08.022
[11] 李京蓉, 周学斌, 马真, 刘泽华, 石国玺, 王文颖, 张中华, 郭美玲, 姚步青, 张春辉, 马丽, 周华坤. 6种高寒牧区禾本科牧草抗旱性研究与评价. 草地学报, 2018, 26(3): 659-665. LI J R, ZHOU X B, MA Z, LIU Z H, SHI G X, WANG W Y, ZHANG Z H, GUO M L, YAO B Q, ZHANG C C, MA L, ZHOU H K. Research and evalution on drought resistance of six grasses in high-cold pastoral area. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(3): 659-665.
[12] 朱教君, 李智辉, 康宏樟, 范业展. 聚乙二醇模拟水分胁迫对沙地樟子松种子萌发影响研究. 应用生态学报, 2005, 16(5): 801-804. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2005.05.005 ZHU J J, LI Z H, KANG H Z, FAN Y Z. Effects of polyethylene glycol (PEG)-simulated drought stress on Pinus sylvestris var. Mongolica seed germination on sandy land. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2005, 16(5): 801-804. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2005.05.005
[13] 施积炎, 丁贵杰. 水分胁迫对不同种源马尾松种子发芽的影响. 山地农业生物学报, 2000, 19(5): 32-337. SHI J Y, DING G J. The effect of water stress on germination of Masson Pine seeds from different provenance. Journal of Mountain Agricultural Biology, 2000, 19(5): 32-337.
[14] 冯淑华, 陈雅君. 干旱对草地早熟禾种子萌发的影响. 草地与草坪, 2006(1): 70-71. FENG S H, CHEN Y J. The influence of drought on seeds' germination ability of Poa pratensis cultivars. Grassland and Lawn, 2006(1): 70-71.
[15] 张志良, 瞿伟菁. 植物生理学实验指导. 3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2005. ZHANG Z L, QU W J. Plant Physiology Experiment Guidance. 3rd Edition. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2005.
[16] 武永军, 何国强, 史艳茹, 梁宗锁. 不同pH值缓冲液处理下蚕豆叶片相对含水量、脯氨酸及丙二醛含量的变化. 干旱地区农业研究, 2009, 27(6): 169-172. WU Y J, HE G Q, SHI Y R, LIANG Z S. The relative water content, proline and malondialdehyde content of broad bean leaves were treated with different pH buffer. Agricultural Research in Arid Regions, 2009, 27(6): 169-172.
[17] 罗志娜, 赵桂琴, 刘欢. 24个燕麦品种种子萌发耐盐性综合评价. 草原与草坪, 2012, 32(1): 34-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5500.2012.01.007 LUO Z N, ZHAO G Q, LIU H. 24 oat varieties of seed germination of salt resistance comprehensive evaluation. Grassland and Lawn, 2012, 32(1): 34-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5500.2012.01.007
[18] 王晓龙. 五种禾本科牧草生物学特性、农艺性状及抗逆性研究. 呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学硕士学位论文, 2014. WANG X L. Evaluation of the biologic traits, agronomic characters and stress tolerance for five forage grasses. Master Thesis. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2014.
[19] 武俊英, 刘景辉, 翟利剑, 李倩, 李立军. 不同品种燕麦种子萌发和幼苗生长的耐盐性. 生态学杂志, 2009, 28(10): 1960-1965. WU J Y, LIU J H, ZHAI L J, LI Q, LI L J. Salt-tolerance of seed germination and seedling growth of different oat varieties. Ecology Journal, 2009, 28(10): 1960-1965.
[20] 史燕山, 骆建霞, 黄家珍, 叶军, 魏巍. 盐胁迫对7种草本地被植物种子萌发的影响. 天津农学院学报, 2007, 14(4): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5394.2007.04.001 SHI Y S, LUO J X, HUANG J Z, YE J, WEI E. Effects of salt stress on seed germination of seven herb ground cover plants. Journal of Tianjin Agricultural College, 2007, 14(4): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5394.2007.04.001
[21] LI M, WANG G X. Effect of drought Stress on activities of cell defense enzymes and lipid peroxidation in glycyrrhiza uralensis seedlings. Acta Ecoloigica Sinica, 2002, 22(4): 503-507.
[22] 陈莎莎, 姚世响, 袁军文, 兰海燕. 盐生植物灰绿藜对NaCl和NaHCO3胁迫的生理响应. 新疆农业科学, 2010, 47(5): 882-887. CHEN S S, YAO S X, YUAN J W, LAN H Y. Physiological responses of halophyte Chenopodium glaucum L. to NaCl and NaHCO3 stresses. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 47(5): 882-887.
[23] 邓敏捷, 张晓申, 范国强, 赵振利, 董焱鹏, 魏振. 四倍体泡桐对盐胁迫生理响应的差异. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2013, 33(11): 42-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-923X.2013.11.008 DENG M J, ZHANG X S, FAN G Q, ZHAO Z L, DONG Y P, WEI Z. Comparative studies on physiological responses to salt stress in tetraploid paulownia plants. Journal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2013, 33(11): 42-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-923X.2013.11.008
[24] 洪森荣, 尹明华. 红芽芋驯化苗对盐胁迫的光合及生理响应. 西北植物学报, 2013, 33(12): 2499-2506. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2013.12.2499 HONG S R, YIN M H. Photosynthetic and physiological responses of red bud taro transplantating seedlings under salt stress. Journal of Northwest Plants, 2013, 33(12): 2499-2506. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2013.12.2499
[25] 廖岩, 陈桂珠. 三种红树植物对盐胁迫的生理适应. 生态学报, 2007, 27(6): 2208-2214. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.06.008 LIAO Y, CHEN G Z. Research on physiological adaptability of three mangrove species to salt stress. Journal of Ecology, 2007, 27(6): 2208-2214. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.06.008
[26] 张丽. 平欧杂种榛抗盐碱生理机制研究及其耐盐性评价. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2015. ZHANG L. Study on the Physiological Mechanism of the Hybrid Hazel and Salinity Tolerance. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry Sciences, 2015.
-
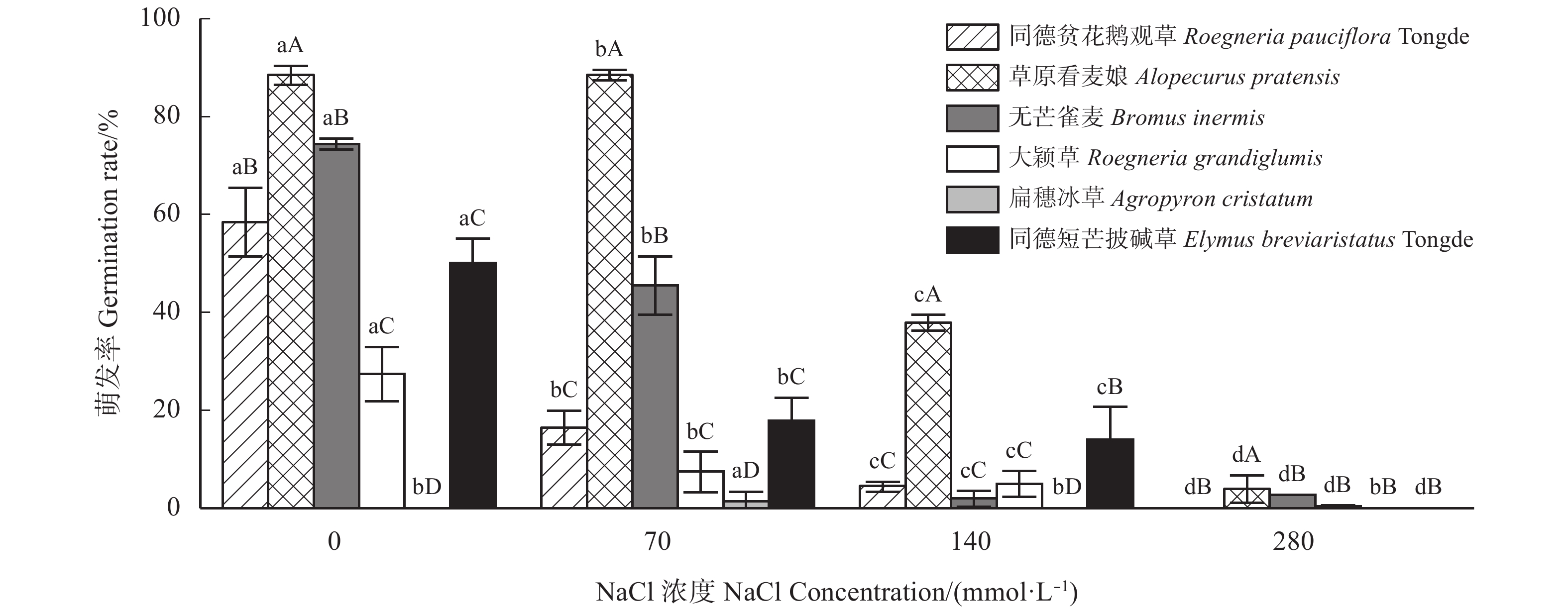
图 1 不同NaCl浓度处理下6种牧草的萌发率
不同小写字母表示同一物种不同NaCl浓度间差异显著(P < 0.05),不同大写字母表示同一NaCl浓度下不同物种间差异显著(P < 0.05)。下同。
Figure 1. Germination rate of 6 pastures under different NaCl concentrations
Different lowercase letters within the same species indicate significant difference between different NaCl concentrations at the 0.05 level, and different capital letters within the same NaCl concentration indicate significant difference between different species at the 0.05 level; similarly for the following tables.
表 1 供试材料
Table 1 Test materials
材料 Material 来源 Source 同德贫花鹅观草 Roegneria pauciflora Tongde 青海省牧草良种繁殖场 Qinghai Province Pasture Breeding Farm 草原看麦娘 Alopecurus pratensis 青海省草原总站 Qinghai Provincial Grassland Station 无芒雀麦 Bromus inermis 青海省草原总站 Qinghai Provincial Grassland Station 大颖草 Roegneria grandiglumis 青海省草原总站 Qinghai Provincial Grassland Station 扁穗冰草 Agropyron cristatum 青海省草原总站 Qinghai Provincial Grassland Station 同德短芒披碱草 Elymus breviaristatus Tongde 青海省牧草良种繁殖场 Qinghai Province Pasture Breeding Farm 表 2 不同NaCl浓度处理下6种牧草丙二醛含量
Table 2 MDA content of six grass species under NaCl treatment
μmol·g–1 物种 Species NaCl浓度 NaCl concentration 0 mmol·L–1 50 mmol·L–1 100 mmol·L–1 150 mmol·L–1 200 mmol·L–1 平均 Average Ⅰ 3.66 ± 0.02Be 7.84 ± 0.02Bd 12.18 ± 0.02Ac 33.27 ± 0.02Ab 45.63 ± 0.01Aa 20.52 ± 0.02A Ⅱ 4.13 ± 0.01Ae 8.63 ± 0.02Ad 11.36 ± 0.02Bc 23.63 ± 0.02Cb 35.28 ± 0.01Ca 16.61 ± 0.02B Ⅲ 3.74 ± 0.00Be 8.33 ± 0.02Bd 10.54 ± 0.02Cc 21.86 ± 0.03Cb 30.43 ± 0.03Da 14.98 ± 0.03C Ⅳ 3.85 ± 0.04Be 7.46 ± 0.02Bd 10.94 ± 0.02Cc 27.28 ± 0.01Bb 39.45 ± 0.03Ba 17.68 ± 0.03B Ⅴ 3.44 ± 0.03Ce 7.28 ± 0.02Cd 11.37 ± 0.03Bc 31.43 ± 0.02Ab 42.36 ± 0.03Aa 19.17 ± 0.03A Ⅵ 3.17 ± 0.02Ce 7.32 ± 0.03Cd 11.46 ± 0.02Ac 24.84 ± 0.04Bb 37.45 ± 0.02BCa 16.85 ± 0.03B Ⅰ:同德贫花鹅观草 Roegneria pauciflora Tongde;Ⅱ:草原看麦娘 Alopecurus pratensis;Ⅲ:无芒雀麦 Bromus inermis;Ⅳ:大颖草 Roegneria grandiglumis;Ⅴ:扁穗冰草 Agropyron cristatum;Ⅵ:同德短芒披碱草 Elymus breviaristatus Tongde。下同Similarly for the following tables. 表 3 NaCl处理下6种牧草叶绿素含量的变化
Table 3 Changes of chlorophyll content of six grass species under NaCl treatment
μg·g–1 物种 Species NaCl浓度 NaCl concentration 0 mmol·L–1 50 mmol·L–1 100 mmol·L–1 150 mmol·L–1 200 mmol·L–1 平均 Average Ⅰ 3.41 ± 0.01Dc 3.90 ± 0.01Da 3.55 ± 0.02Db 2.97 ± 0.02Dd 0.53 ± 0.01De 3.08 ± 0.01D Ⅱ 5.40 ± 0.02Bc 7.95 ± 0.01Ba 6.34 ± 0.03Bb 3.62 ± 0.01Bd 2.73 ± 0.01Be 5.21 ± 0.02B Ⅲ 7.42 ± 0.01Ac 9.24 ± 0.02Aa 8.77 ± 0.01Ab 4.23 ± 0.02Ad 3.94 ± 0.03Ae 6.72 ± 0.02A Ⅳ 3.70 ± 0.01Cc 5.43 ± 0.02Ca 4.57 ± 0.02Cb 3.07 ± 0.01Cd 1.50 ± 0.02Ce 3.69 ± 0.02C Ⅴ 3.63 ± 0.02Dc 4.56 ± 0.01Da 3.98 ± 0.02Db 3.02 ± 0.01Dd 1.07 ± 0.02De 3.14 ± 0.02D Ⅵ 4.07 ± 0.02Cc 5.36 ± 0.02Ca 4.55 ± 0.01Cb 3.77 ± 0.02Cd 1.60 ± 0.02Ce 3.85 ± 0.02C 表 4 NaCl处理下 6 种牧草可溶性糖含量的变化
Table 4 Changes of soluble sugar content of six grass species under NaCl treatment
mmol·g–1 物种 Species NaCl浓度 NaCl concentration 0 mmol·L–1 50 mmol·L–1 100 mmol·L–1 150 mmol·L–1 200 mmol·L–1 平均 Average Ⅰ 7.26 ± 0.02Dd 7.51 ± 0.02Dc 10.96 ± 0.02Da 8.74 ± 0.01Db 4.97 ± 0.01De 7.89 ± 0.02D Ⅱ 11.45 ± 0.01Ad 12.75 ± 0.03Ab 14.95 ± 0.01Ba 12.47 ± 0.02Bc 9.33 ± 0.01Be 12.19 ± 0.02B Ⅲ 10.45 ± 0.00Bd 12.67 ± 0.02Bc 20.15 ± 0.01Aa 14.69 ± 0.03Ab 10.23 ± 0.02Ae 13.64 ± 0.02A Ⅳ 9.08 ± 0.01Cd 11.23 ± 0.02Cc 14.03 ± 0.02Ca 11.79 ± 0.01Cb 5.39 ± 0.01Ce 10.30 ± 0.01C Ⅴ 7.43 ± 0.02Dd 8.88 ± 0.01Dc 11.34 ± 0.02Da 9.37 ± 0.02Db 2.77 ± 0.02De 7.96 ± 0.02D Ⅵ 8.98 ± 0.01Cd 10.63 ± 0.02Cc 12.99 ± 0.00Ca 10.96 ± 0.01Cb 5.77 ± 0.02Ce 9.87 ± 0.02C 表 5 NaCl处理下 6 种牧草脯氨酸含量的变化
Table 5 Changes of proline content of six grass species under NaCl treatment
μg·g–1 物种 Species NaCl浓度 NaCl concentration 0 mmol·L–1 50 mmol·L–1 100 mmol·L–1 150 mmol·L–1 200 mmol·L–1 平均 Average Ⅰ 3.44 ± 0.00Ce 8.73 ± 0.02Ad 9.84 ± 0.02Cc 14.46 ± 0.03Cb 20.57 ± 0.03Ca 11.81 ± 0.02C Ⅱ 3.54 ± 0.03Be 7.88 ± 0.02Bd 11.67 ± 0.01Ac 18.46 ± 0.02Ab 25.37 ± 0.02Aa 13.38 ± 0.02A Ⅲ 3.86 ± 0.02Be 7.74 ± 0.02Bd 12.78 ± 0.02Ac 17.38 ± 0.02Ab 27.04 ± 0.01Aa 13.76 ± 0.02A Ⅳ 3.45 ± 0.03Ce 7.66 ± 0.02Bd 10.84 ± 0.02Bc 17.18 ± 0.01Bb 24.36 ± 0.03Ba 12.67 ± 0.02B Ⅴ 4.33 ± 0.01Ae 8.23 ± 0.02Ad 11.86 ± 0.02Bc 15.73 ± 0.03Bb 20.14 ± 0.16Ba 12.06 ± 0.05B Ⅵ 3.47 ± 0.02Ce 7.45 ± 0.03Cd 11.76 ± 0.02Bc 16.46 ± 0.03Bb 23.98 ± 0.05Ba 12.62 ± 0.04B 表 6 各牧草对NaCl处理适应指标的隶属函数值及评价
Table 6 Membership value and evaluation of adaptation indexes of herbage to NaCl treatment
物种
Grass species发芽率
Germination rateMDA 含量
MDA content叶绿素
Chlorophyll可溶性糖
Soluble sugar脯氨酸
Proline总隶属函数值
Total membership
function value排序
Sort同德贫花鹅观草
Roegneria pauciflora Tongde0.337 0.119 0.438 0.443 0.475 0.362 6 草原看麦娘
Alopecurus pratensis0.387 0.182 0.528 0.514 0.462 0.415 2 无芒雀麦
Bromus inermis0.424 0.197 0.598 0.475 0.537 0.446 1 大颖草
Roegneria grandiglumis0.363 0.165 0.476 0.481 0.572 0.411 3 扁穗冰草
Agropyron cristatum0.361 0.129 0.447 0.454 0.514 0.381 5 同德短芒披碱草
Elymus breviaristatus Tongde0.355 0.143 0.488 0.472 0.498 0.391 4 -
[1] VEERANAGAMALLAIAH G, CHANDRAOBULREDDY P, JYOTHSNAKUMARI G, SUDHAKAR C. Glutamine synthetase expression and pyrrotine-5-carboxylate reductase activity influence proline accumulation in two cultivars of foxtail millet (Setaria italica L. ) with differential salt sensitivity. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2007, 60: 239-244. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2006.10.012
[2] BARTELS D, SUNKAR R. Drought and salt tolerance in plants. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 2005, 24: 23-58. doi: 10.1080/07352680590910410
[3] 乔枫, 罗桂花, 耿贵工. 蚕豆幼苗对NaCI和NaHCO3胁迫的生理响应. 安徽农业大学学报, 2011, 38(5): 783-787. QIAO F, LUO G H, GEN G G. Physiological responses of vicia faba seedlings to NaCl and NaHCO3 stress. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2011, 38(5): 783-787.
[4] MELONI D A, OLIVA M A, MARTINEZ C A. Photosynthesis and activity of superoxide dismutase, peroxidese and glutathione reductase in cotton under salt stress. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2003, 49: 69-76. doi: 10.1016/S0098-8472(02)00058-8
[5] 陈惠哲, NATALIA LADATKO, 朱德峰, 林贤青, 张玉屏, 孙宗修. 盐胁迫下水稻苗期Na+和K+吸收与分配规律的初步研究. 植物生态学报, 2007, 31(5): 937-945. CHEN H Z, NATALIA L, ZHU D F, LIN X Q, ZHANG Y P, SUN Z X. Absorption and diatribution of Na+ and K+ in rice seedline under salt stress. Journal of Plant Ecology, 2007, 31(5): 937-945.
[6] 乔旭, 黄爱军, 褚贵新. 植物对盐分胁迫的响应及其耐盐机理研究进展. 新疆农业科学, 2011, 48(11): 2089-2094. doi: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2011.11.023 QIAO X, HUANG A J, CHU G X. Research progress in the effects of salt stress on plant and the mechanism of plant resistance. Agriculture Science of Xinjiang, 2011, 48(11): 2089-2094. doi: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2011.11.023
[7] 沈艳, 谢应忠. 牧草抗旱性和耐盐性研究进展. 宁夏农学院学报, 2004, 25(1): 65-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0747.2004.01.019 SHEN Y, XIE Y Z. The progress of studies on forage grass drought resistance and salt tolerance. Journal of Ningxia Agricultural College, 2004, 25(1): 65-69. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0747.2004.01.019
[8] 余玲, 王彦荣, 孙建华. 野大麦种子萌发条件及抗逆性研究. 草业学报, 1999, 8(1): 50-57. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-5759.1999.01.008 YU L, WANG Y R, SUN J H. Studies on germination condition and stress resistance of Hordeum brevisubulatum seeds. Journal of Grass Industry, 1999, 8(1): 50-57. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-5759.1999.01.008
[9] 毛培春, 王勇. 不同禾本科牧草材料种子萌发的耐盐性试验. 内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2004(2): 115-118. MAO P C, WANG Y. Experiment on salt resistance in seed germination stage of six grass varieties. Journal of Inner Mongolia Agricultural University (Natural Science Edition), 2004(2): 115-118.
[10] 王晓龙, 李红, 闫利军, 米福贵, 于洁, 贾振宇, 杨曌, 杨伟光. 5种禾本科牧草种子萌发及幼苗耐盐性鉴定. 种子, 2016(8): 27-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2690.2016.08.022 WANG X L, LI H, YAN L J, MI F G, YU J, JIA Z Y, YANG Z, YANG W G. Salt-tolerance of seed germination and seedling growth for five grass species. Seeds, 2016(8): 27-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2690.2016.08.022
[11] 李京蓉, 周学斌, 马真, 刘泽华, 石国玺, 王文颖, 张中华, 郭美玲, 姚步青, 张春辉, 马丽, 周华坤. 6种高寒牧区禾本科牧草抗旱性研究与评价. 草地学报, 2018, 26(3): 659-665. LI J R, ZHOU X B, MA Z, LIU Z H, SHI G X, WANG W Y, ZHANG Z H, GUO M L, YAO B Q, ZHANG C C, MA L, ZHOU H K. Research and evalution on drought resistance of six grasses in high-cold pastoral area. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(3): 659-665.
[12] 朱教君, 李智辉, 康宏樟, 范业展. 聚乙二醇模拟水分胁迫对沙地樟子松种子萌发影响研究. 应用生态学报, 2005, 16(5): 801-804. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2005.05.005 ZHU J J, LI Z H, KANG H Z, FAN Y Z. Effects of polyethylene glycol (PEG)-simulated drought stress on Pinus sylvestris var. Mongolica seed germination on sandy land. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2005, 16(5): 801-804. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2005.05.005
[13] 施积炎, 丁贵杰. 水分胁迫对不同种源马尾松种子发芽的影响. 山地农业生物学报, 2000, 19(5): 32-337. SHI J Y, DING G J. The effect of water stress on germination of Masson Pine seeds from different provenance. Journal of Mountain Agricultural Biology, 2000, 19(5): 32-337.
[14] 冯淑华, 陈雅君. 干旱对草地早熟禾种子萌发的影响. 草地与草坪, 2006(1): 70-71. FENG S H, CHEN Y J. The influence of drought on seeds' germination ability of Poa pratensis cultivars. Grassland and Lawn, 2006(1): 70-71.
[15] 张志良, 瞿伟菁. 植物生理学实验指导. 3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2005. ZHANG Z L, QU W J. Plant Physiology Experiment Guidance. 3rd Edition. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2005.
[16] 武永军, 何国强, 史艳茹, 梁宗锁. 不同pH值缓冲液处理下蚕豆叶片相对含水量、脯氨酸及丙二醛含量的变化. 干旱地区农业研究, 2009, 27(6): 169-172. WU Y J, HE G Q, SHI Y R, LIANG Z S. The relative water content, proline and malondialdehyde content of broad bean leaves were treated with different pH buffer. Agricultural Research in Arid Regions, 2009, 27(6): 169-172.
[17] 罗志娜, 赵桂琴, 刘欢. 24个燕麦品种种子萌发耐盐性综合评价. 草原与草坪, 2012, 32(1): 34-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5500.2012.01.007 LUO Z N, ZHAO G Q, LIU H. 24 oat varieties of seed germination of salt resistance comprehensive evaluation. Grassland and Lawn, 2012, 32(1): 34-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5500.2012.01.007
[18] 王晓龙. 五种禾本科牧草生物学特性、农艺性状及抗逆性研究. 呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学硕士学位论文, 2014. WANG X L. Evaluation of the biologic traits, agronomic characters and stress tolerance for five forage grasses. Master Thesis. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2014.
[19] 武俊英, 刘景辉, 翟利剑, 李倩, 李立军. 不同品种燕麦种子萌发和幼苗生长的耐盐性. 生态学杂志, 2009, 28(10): 1960-1965. WU J Y, LIU J H, ZHAI L J, LI Q, LI L J. Salt-tolerance of seed germination and seedling growth of different oat varieties. Ecology Journal, 2009, 28(10): 1960-1965.
[20] 史燕山, 骆建霞, 黄家珍, 叶军, 魏巍. 盐胁迫对7种草本地被植物种子萌发的影响. 天津农学院学报, 2007, 14(4): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5394.2007.04.001 SHI Y S, LUO J X, HUANG J Z, YE J, WEI E. Effects of salt stress on seed germination of seven herb ground cover plants. Journal of Tianjin Agricultural College, 2007, 14(4): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5394.2007.04.001
[21] LI M, WANG G X. Effect of drought Stress on activities of cell defense enzymes and lipid peroxidation in glycyrrhiza uralensis seedlings. Acta Ecoloigica Sinica, 2002, 22(4): 503-507.
[22] 陈莎莎, 姚世响, 袁军文, 兰海燕. 盐生植物灰绿藜对NaCl和NaHCO3胁迫的生理响应. 新疆农业科学, 2010, 47(5): 882-887. CHEN S S, YAO S X, YUAN J W, LAN H Y. Physiological responses of halophyte Chenopodium glaucum L. to NaCl and NaHCO3 stresses. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 47(5): 882-887.
[23] 邓敏捷, 张晓申, 范国强, 赵振利, 董焱鹏, 魏振. 四倍体泡桐对盐胁迫生理响应的差异. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2013, 33(11): 42-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-923X.2013.11.008 DENG M J, ZHANG X S, FAN G Q, ZHAO Z L, DONG Y P, WEI Z. Comparative studies on physiological responses to salt stress in tetraploid paulownia plants. Journal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology, 2013, 33(11): 42-46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-923X.2013.11.008
[24] 洪森荣, 尹明华. 红芽芋驯化苗对盐胁迫的光合及生理响应. 西北植物学报, 2013, 33(12): 2499-2506. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2013.12.2499 HONG S R, YIN M H. Photosynthetic and physiological responses of red bud taro transplantating seedlings under salt stress. Journal of Northwest Plants, 2013, 33(12): 2499-2506. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2013.12.2499
[25] 廖岩, 陈桂珠. 三种红树植物对盐胁迫的生理适应. 生态学报, 2007, 27(6): 2208-2214. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.06.008 LIAO Y, CHEN G Z. Research on physiological adaptability of three mangrove species to salt stress. Journal of Ecology, 2007, 27(6): 2208-2214. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2007.06.008
[26] 张丽. 平欧杂种榛抗盐碱生理机制研究及其耐盐性评价. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2015. ZHANG L. Study on the Physiological Mechanism of the Hybrid Hazel and Salinity Tolerance. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry Sciences, 2015.



 下载:
下载:

