黄河上游白河干流全段植物群落特征及生物多样性
English
-
参考文献
[1] 韩路, 王海珍, 于军. 河岸带生态学研究进展与展望. 生态环境学报, 2013, 22(5): 879-886. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2013.05.026 HAN L, WANG H Z, YU J. Research progress and prospects on riparian zone ecology. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2013, 22(5): 879-886. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2013.05.026
[2] 周铭浩, 邱静, 洪昌红, 杜欢欢, 汤海平. 河岸带功能及其保护修复措施. 黄河水利职业技术学院学报, 2019, 31(4): 6-11. doi: 10.13681/j.cnki.cn41-1282/tv.2019.04.002 ZHOU M H, QIU J, HONG C H, DU H H, TANG H P. Riparian zone function and its protection and remediation measures. Journal of Yellow River Conservancy Technical Institute, 2019, 31(4): 6-11. doi: 10.13681/j.cnki.cn41-1282/tv.2019.04.002
[3] 余飞燕, 王坤悦, 叶鑫, 董洪君, 黄凯, 罗志力, 郝建锋. 金马河温江段河岸带不同生境草本群落物种多样性和生物量变化研究. 草地学报, 2020, 28(3): 793-800. YU F Y, WANG K Y, YE X, DONG H J, HUANG K, LUO Z L, HAO J F. Research on species diversity and biomass variation of herbaceous communityin difference habitats in Wenjiang Section of Jinma River. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(3): 793-800.
[4] 曾艳. 不同土地利用类型下河岸带草本植物群落结构及其影响因素. 南京: 南京大学硕士学位论文, 2015. ZENG Y. The effects of land use on herbaceouscommunity structure in the riparian zone. Master Thesis. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2015
[5] 张建春, 彭补拙. 河岸带及其生态重建研究. 地理研究, 2002(3): 373-383. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2002.03.013 ZHANG J C, PENG B Z. Research on riparian zone and its ecological reconstruction. Geographical Studies, 2002(3): 373-383. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2002.03.013
[6] 邓红兵, 王青春, 王庆礼, 吴文春, 邵国凡. 河岸植被缓冲带与河岸带管理. 应用生态学报, 2001(6): 951-954. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2001.06.035 DENG H B, WANG Q C, WANG Q L, WU W C, SHAO G F. Riparian vegetation buffer zone and riparian zone management. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2001(6): 951-954. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2001.06.035
[7] CHANG T P, TOEBES G H. A statistical comparison of meander planforms in the Wabash Basin. Water Resources Research, 1970, 6(2): 557-578.
[8] SWAMEE P K, PARKASH B, THOMAS J V, SINGH S. Changes in channel pattern of river ganga between mustafabad and rajmahal, gangetic plains since 18th century. International Journal of Sediment Research, 2003, 13(3): 219-231.
[9] 刘成, 刘桉, 徐梦珍. 白河河湾迁移速率及影响因素分析. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 2018, 16(5): 495-502, 509. doi: 10.13244/j.cnki.jiwhr.2018.05.020 LIU C, LIU A, XU M Z. Analysis on migration rate and influencing factors of Baihe Bay. Journal of China Academy of Water Resources and Hydropower Sciences, 2018, 16(5): 495-502, 509. doi: 10.13244/j.cnki.jiwhr.2018.05.020
[10] 杜际增, 王根绪, 李元寿. 近45年长江黄河源区高寒草地退化特征及成因分析. 草业学报, 2015, 24(6): 5-15. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2014302 DU J Z, WANG G X, LI Y S. Degradation characteristics and causes of alpine grasslands in the source region of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers in recent 45 years. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(6): 5-15. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2014302
[11] 薛娴, 郭坚, 张芳, 宗莉, 韩邦帅, 黄翠华. 高寒草甸地区沙漠化发展过程及成因分析: 以黄河源区玛多县为例. 中国沙漠, 2007(5): 725-732. XUE X, GUO J, ZHANG F, ZONG L, HAN B S, HUANG C H. Development and cause of aeolian desertification in Alpine Region: In case of Maduo County in Yellow River Source Area. Journal of Desert Research, 2007(5): 725-732.
[12] KAWAI S, JULIEN P Y. Point bar deposits in narrow sharp bends. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 1996, 34(2): 205-218. doi: 10.1080/00221689609498497
[13] 杨玥, 李志威, 胡旭跃, 吴新宇. 黄河源白河与黑河下游凸岸点边滩形态与变化规律. 泥沙研究, 2021, 46(1): 50-56, 17. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2021.01.007 YANG Y, LI Z W, HU X Y, WU X Y. Morphological characteristics and processes of point bars in the lower White and Black Rivers of the Yellow River Source region. Journal of Sediment Research, 2021, 46(1): 50-56, 17. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2021.01.007
[14] CZORTEK P, DYDERSKI M K, JAGODZINSKI A M. River regulation drives shifts in urban riparian vegetation over three decades. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2019, 47: 126542.
[15] 曲晓涵, 王雪岩. 大连市河岸带生态恢复与植被重建研究. 科技经济导刊, 2019, 27(20): 113. QU X H, WANG X Y. Research on ecological restoration and vegetation reconstruction of Riparian Zone in Dalian City. Technology and Economic Guide, 2019, 27(20): 113.
[16] 胡彬, 翟文静, 赵警卫. 河岸带植被对河流生态功能影响研究进展. 福建林业科技, 2015, 42(3): 233-239. HU B, ZHAI W J, ZHAO J W. Progresses in researches on the influence of riparian vegetation on river ecological functions. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 2015, 42(3): 233-239.
[17] 武晓倩, 范保硕, 滕叶文, 李荣琦, 渠开跃, 钱金平, 田冰. 白洋淀流域河岸带草本植物群落分布特征与土壤环境因子的关系. 应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28(6): 1608-1614. doi: 10.19675/j.cnki.1006-687x.2021.05043 WU X Q, FAN B S, TENG Y W, LI R Q, QU K Y, QIAN J P, TIAN B. Relationship between herbaceous community distribution and soil environmental factors in riparian zone of Baiyangdian River Basin. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2022, 28(6): 1608-1614. doi: 10.19675/j.cnki.1006-687x.2021.05043
[18] 杨树青, 白玉川, 徐海珏, 黄哲. 河岸植被覆盖影响下的河流演化动力特性分析. 水利学报, 2018, 49(8): 995-1006. YANG S Q, BAI Y C, XU H Y, HUANG Z. Dynamic characteristics of river evolution under the influence of riparian vegetation cover. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2018, 49(8): 995-1006.
[19] 朱海丽, 胡夏嵩, 李志威, 刘亚斌. 黄河源区弯曲河道草甸型植被分布特征. 泥沙研究, 2018, 43(1): 58-65. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2018.01.010 ZHU H L, HU X S, LI Z W, LIU Y B. Zoning characteristics and processes in convex bank of meander reaches with riparian meadow in source region of the Yellow River. Journal of Sediment Research, 2018, 43(1): 58-65. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2018.01.010
[20] 刘桉. 黄河源区典型弯曲河流演变与滨河植被的作用研究. 北京: 中国水利水电科学研究院硕士学位论文, 2018. LIU A. Relation between riparian vegetation and meander migration for typical meaning rivers in the Yellow River source region. Master Thesis. Beijing: China Academy of Water Resources and Hydropower Sciences, 2018.
[21] 赵资乐. 黄河上游黑河、白河流域水沙规律. 甘肃水利水电技术, 2005(4): 336-338, 350. ZHAO Z L. The regularity of water and sediment in the Heihe and Baihe river basins in the upper reaches of the Yellow River. Gansu Water Resources and Hydropower Technology, 2005(4): 336-338, 350.
[22] 李志威, 王兆印, 李艳富, 刘乐. 黄河源区典型弯曲河流的几何形态特征. 泥沙研究, 2012(4): 11-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0468-155X.2012.04.003 LI Z W, WANG Z Y, LI Y F, LIU L. Geometric characteristics of typical curved rivers in the source region of the Yellow River. Journal of Sediment Research, 2012(4): 11-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0468-155X.2012.04.003
[23] 方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 唐志尧, 贺金生, 于丹, 江源, 王志恒, 郑成洋, 朱江玲, 郭兆迪. 植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(6): 533-548. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09253 FANG J Y, WANG X P, SHEN Z H, TANG Z Y, HE J S, YU D, JIANG Y, WANG Z H, ZHENG C Y, ZHU J L, GUO Z D. Main contents, methods and technical specifications of plant community inventory. Biodiversity Science, 2009, 17(6): 533-548. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09253
[24] LIN T, DONG S, SHERMAN R, LIU S, WU X. Changes in vegetation composition and plant diversity with rangeland degradation in the alpine region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. The Rangeland Journal, 2015, 37(1): 107-115. doi: 10.1071/RJ14077
[25] 张帆, 李元淳, 王新, 朱剑霄. 青藏高原高寒草甸退化对草地群落生物量及其分配的影响. 草业科学, 2021, 38(8): 1451-1458. doi: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2020-0710 ZHANG F, LI Y C, WANG X, ZHU J X. Effect of rangeland degradation on biomass allocation in alpine meadows on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(8): 1451-1458. doi: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2020-0710
[26] 李成阳, 张文娟, 赖炽敏, 彭飞, 陈小杰, 薛娴, 王涛, 尤全刚, 杜鹤强. 黄河源区不同退化程度高寒草原群落生产力、物种多样性和土壤特性及其关系研究. 生态学报, 2021, 41(11): 4541-4551. LI C Y, ZHANG W J, LAI C M, PENG F, CHEN X J, XUE X, WANG T, YOU Q G, DU H Q. Plant productivity, species diversity, soil properties, and their relationships in an alpine steppe under different degradation degrees at the source of the Yellow River. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(11): 4541-4551.
[27] 陈影, 陈苏, 马鸿岳, 单岳, 冯天朕, 张鸿龄. 辽河干流河岸带植物及微生物多样性研究. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(9): 2048-2057. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0311 CHEN Y, CHEN S, MA H Y, SHAN Y, FENG T Z, ZHANG H L. Plant and microbial diversity in the riparian zone of the Liao River mainstream, China. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(9): 2048-2057. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0311
[28] 富金赤, 李晓莎, 许中旗, 郭延朋, 赵娱, 李校. 冀北山地阳坡草本植物物种多样性的空间异质性研究. 草地学报, 2018, 26(6): 1298-1304. FU J C, LI X S, XU Z Q, GUO Y P, ZHAO Y, LI X. Spatial heterogeneity of herbaceous plant species diversity in dry south-slope of North Mountain of Hebei. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(6): 1298-1304.
[29] 何松. 嘉陵江中下游河岸植被及植物多样性研究. 重庆: 西南大学硕士学位论文, 2019. HE S. Research on riparian vegetation and plant diversity in the middle and lower reaches of Jialing River. Master Thesis. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2019.
[30] 孔庆仙, 信忠保, 夏晓平. 北京怀九河河岸带植物多样性及影响因子分析. 科技导报, 2017, 35(24): 57-65. KONG Q X, XIN Z B, XIA X P. Analysis of plant diversity and influencing factors in the riparian zone of Huaijiu River in Beijing. Science & Technology Review, 2017, 35(24): 57-65.
[31] 汪殿蓓, 暨淑仪, 陈飞鹏. 植物群落物种多样性研究综述. 生态学杂志, 2001, 20(4): 55-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2001.04.015 WANG D B, JI S Y, CHEN F P. A review of studies on plant community species diversity. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2001, 20(4): 55-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2001.04.015
[32] WANG C T, LONG R J, WANG Q L, JING Z C, SHI J J. Changes in plant diversity, biomass and soil C, in alpine meadows at different degradation stages in the headwater region of three rivers, China. Land Degradation & Development, 2009, 20(2): 187-198.
[33] LI C Y, PENG F, XUE X, YOU Q G, LAI C M, ZHANG W J, CHENG Y X. Productivity and quality of alpine grassland vary with soil water availability under experimental warming. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 1790.
[34] 李成阳, 赖炽敏, 彭飞, 薛娴, 尤全刚, 张文娟, 刘斐耀. 青藏高原北麓河流域不同退化程度高寒草甸生产力和群落结构特征. 草业科学, 2019, 36(4): 1044-1052. LI C Y, LAI C M, PENG F, XUE X, YOU Q G, ZHANG W J, LIU F Y. Alpine meadows at different stages of degradation in the Beiluhe Basin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Productivity and community structure characteristics. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(4): 1044-1052.
[35] 朱海丽, 王兆印, 李志威. 黄河源区滨河草甸对弯曲河流河道演变的影响. 人民黄河, 2013, 35(4): 41-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2013.04.015 ZHU H L, WANG Z Y, LI Z W. Influence of riparian meadow to the Meandering Rivers evolution in the Yellow River Source Region. Yellow River, 2013, 35(4): 41-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2013.04.015
[36] 谢彬山, 朱海丽, 李本锋, 胡夏嵩. 黄河源区曲流滨河植被空间分布与土壤特性关系研究. 泥沙研究, 2019, 44(6): 66-73. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2019.06.011 XIE B S, ZHU H L, LI B F, HU X S. Study on relationship between vegetation spatial distribution and soil properties in the meander riverside in source region of the Yellow River. Journal of Sediment Research, 2019, 44(6): 66-73. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2019.06.011
[37] 朱海丽. 黄河源区弯曲河流滨河植被增强河岸稳定作用机理研究. 西宁: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院青海盐湖研究所)博士学位论文, 2018. ZHU H L. Study on the mechanism of riverbank stabilization reinforcement by the riparian vegetation of meandering river in the Yellow River source region. PhD Thesis. Xining: Chinese Academy of Sciences (Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2018
[38] 王丹阳. 青藏高原弯曲河流地貌单元对有机碳迁移的影响规律和机制. 长沙: 湖南大学博士学位论文, 2020. WANG D Y. Pattern and mechanism of influence of geomorphic units within meandering river of the Tibetan Plateau on organic carbon transport. PhD Thesis. Changsha: Hunan University, 2020.
[39] 张文丽, 夏会娟, 张远, 孔维静, 贾晓波, 姚懿函. 东辽河河岸带草本植物物种多样性及群落数量分析. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(5): 1142-1149. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.2014.0121 ZHANG W L, XIA H J, ZHANG Y, KONG W J, JIA X B, YAO Y H. Herbaceous species diversity and community quantitative analysis in the riparian zone of East Liaohe River. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(5): 1142-1149. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.2014.0121
[40] 陈吉泉. 河岸植被特征及其在生态系统和景观中的作用. 应用生态学报, 1996, 7(4): 439-448. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.1996.0086 CHEN J Q. Riparian vegetation characteristics and their functions in ecosystems and landscapes. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 1996, 7(4): 439-448. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.1996.0086
[41] 李良涛. 农田边界和居民庭院植物多样性分布格局及植被营建. 北京: 中国农业大学博士学位论文, 2014. LI L T. Distribution pattern of plant diversity and vegeta-tion construction in field margins and homegarden. PhD Thesis. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2014.
-
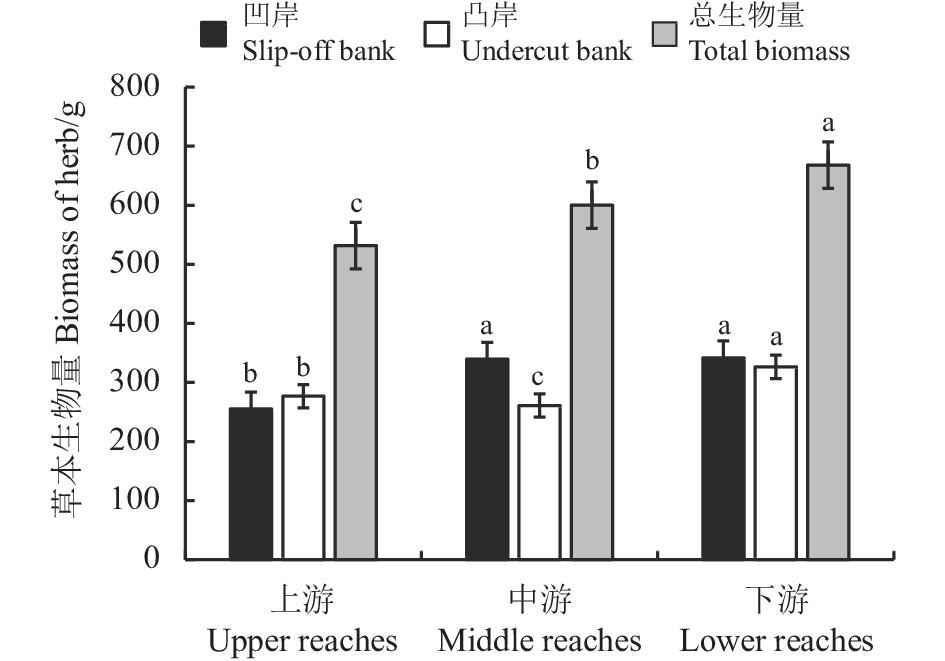
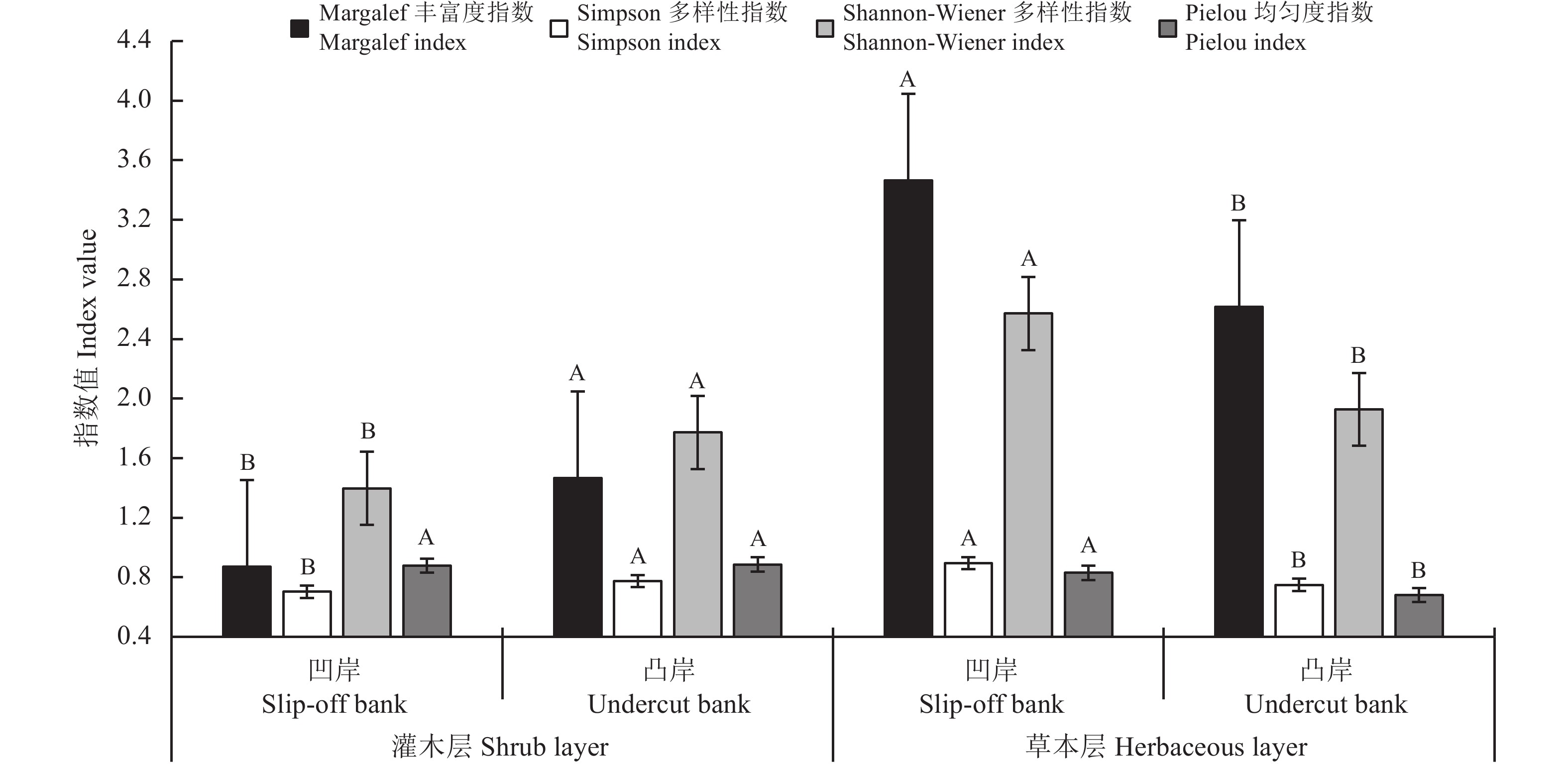
图 3 白河干流全段/凹凸岸植被群落的高度、盖度
不同小写字母表示同一植被不同河段生境间的差异显著(P < 0.05);不同大写字母表示同一植被凹凸岸生境间的差异显著(P < 0.05)。
Figure 3. Height and coverage of communities on the slip-off banks and in riparian zones along the channel of the Baihe River
Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among habitats in different reaches at the 0.05 level; different capital letters indicate significant differences among habitats on slip-off/undercut bank at the 0.05 level.
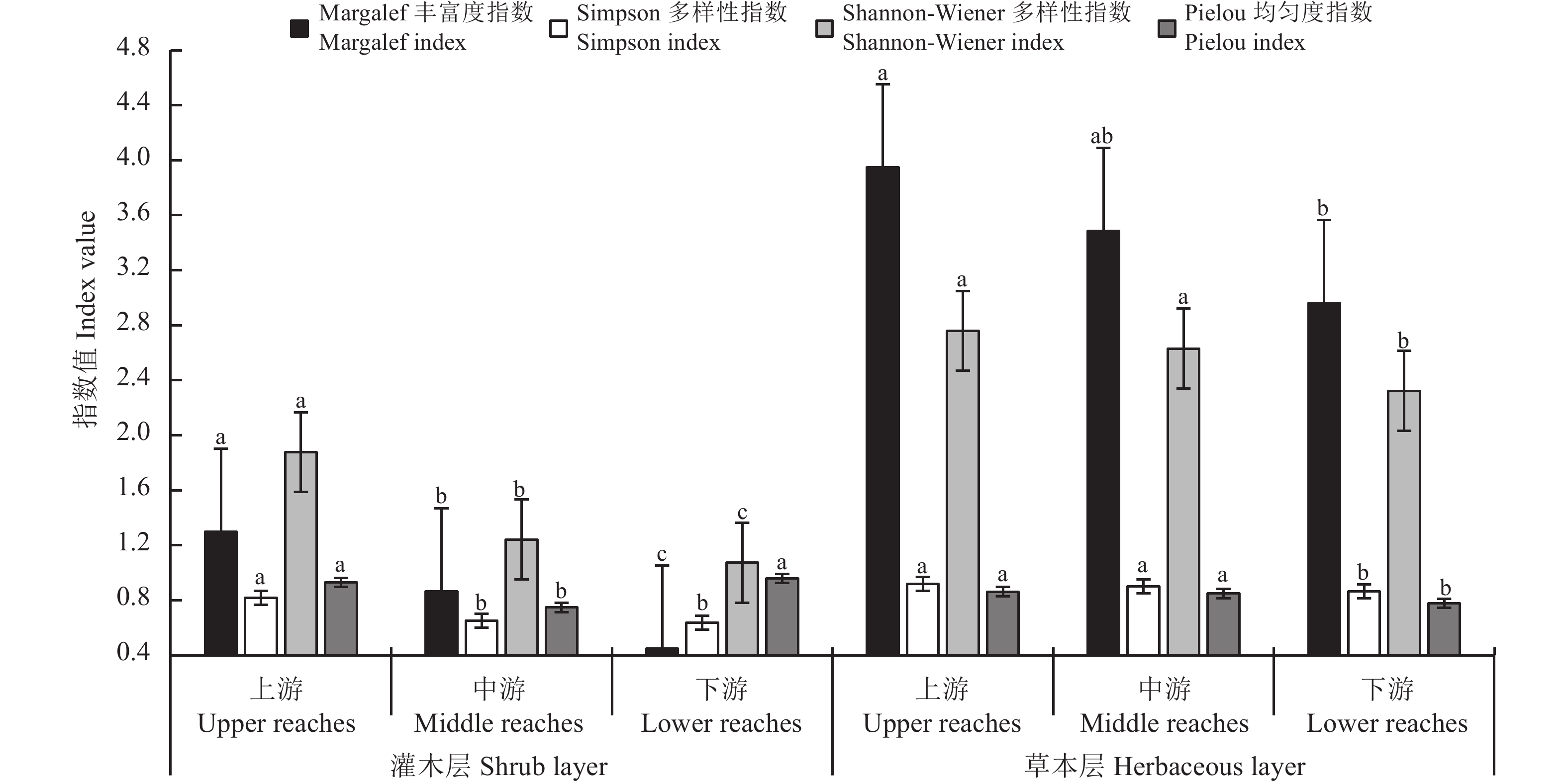
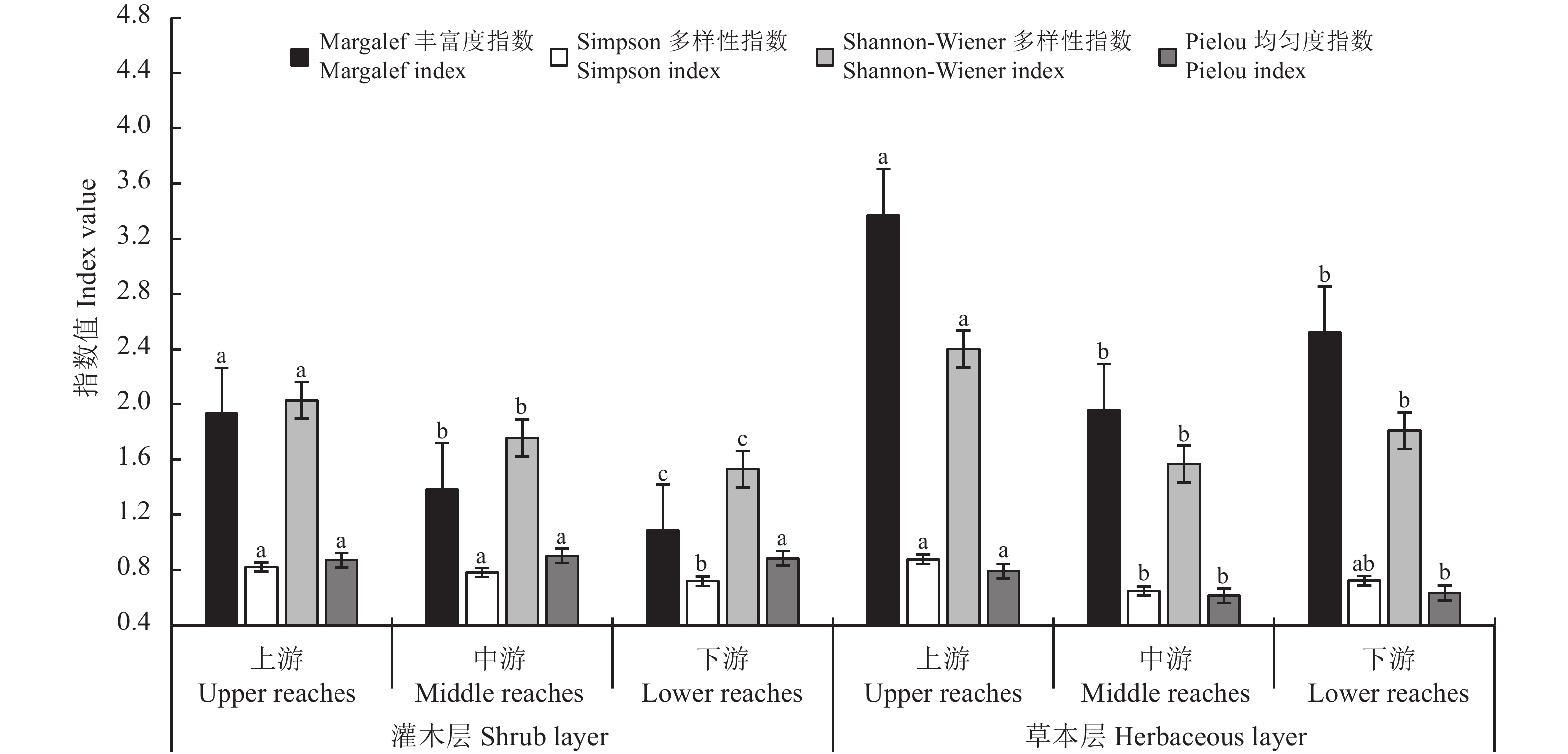
图 5 白河干流全段凹岸植被群落物种多样性
不同小写字母表示同一植被不同河段生境间的差异显著(P < 0.05);图6同。
Figure 5. Species diversity on the slip-off banks in riparian zones along the channel of the Baihe River
Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among habitats in different reaches at the 0.05 level. This is applicable for Figure 6 as well.
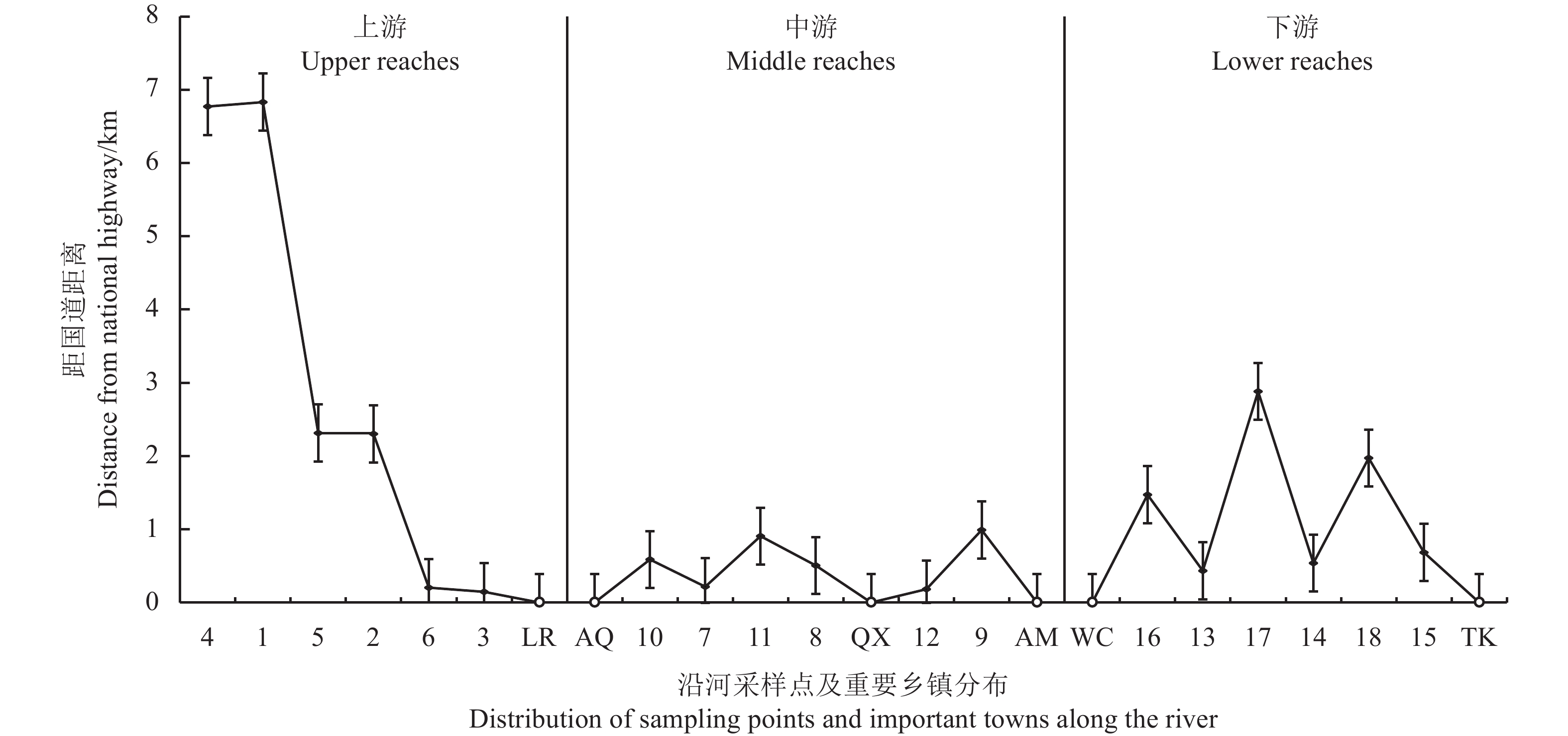
图 9 采样点与国道248的距离
LR:龙日乡;AQ:安曲镇;QX:邛溪镇;AM:阿木乡;WC:瓦切镇;TK:唐克镇。横坐标数字与本研究表1样地编号一致。
Figure 9. Distance between the sampling point and National Highway 248
LR: Longri Township; AQ: Anqu town; QX: Qiongxi town; AM: Amu Township; WC: Wache Township; TK: Tangke Town. The abscissa number is consistent with the sample plot number in Table 1.
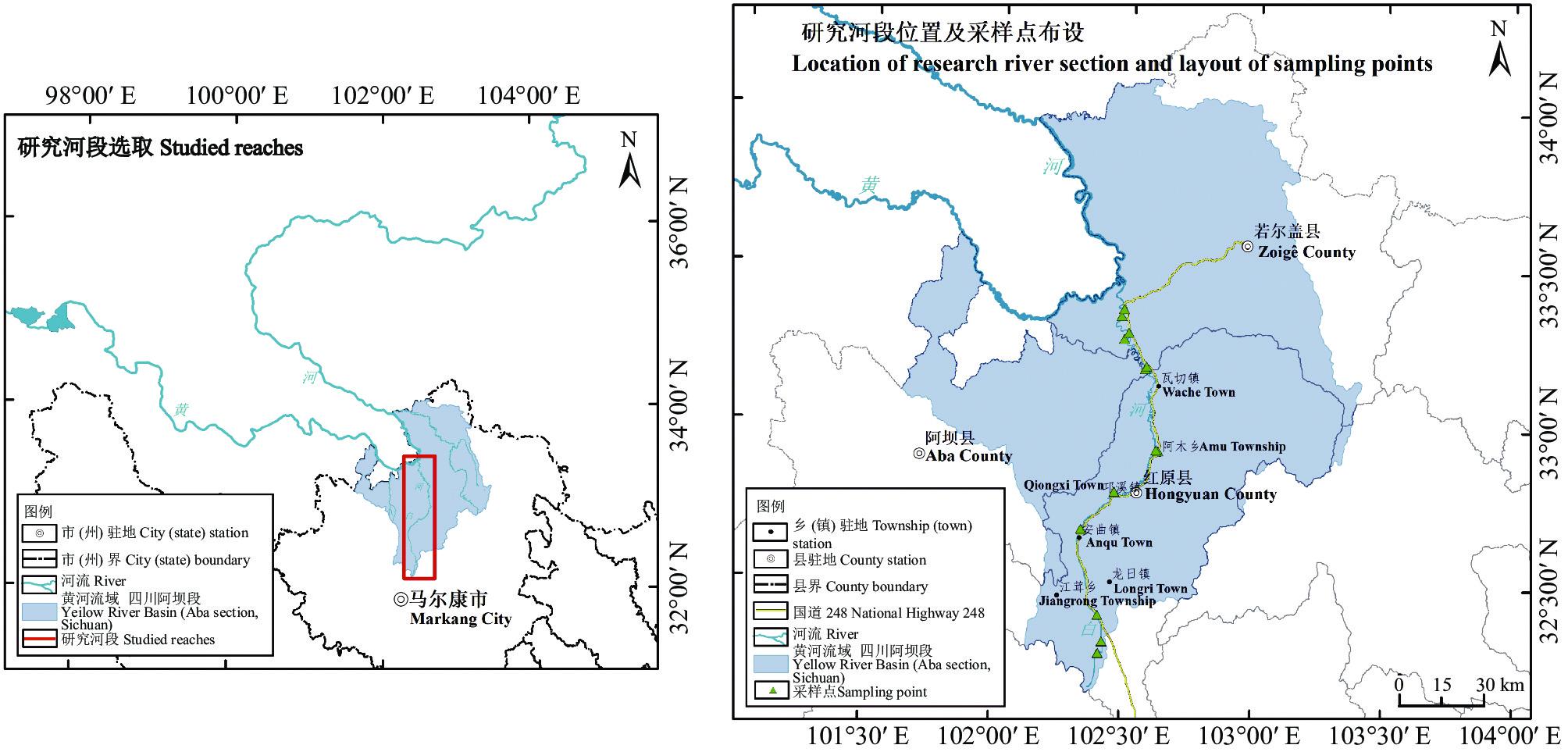
表 1 样地概况
Table 1 Details of the sample plots
生境类型 Habitat type 样地
Sample plot经纬度
Longitude and latitude海拔
Altitude/m河段
Studied reaches凹凸岸
Slip-off/undercut bank上游
Upper reaches凹岸 Slip-off bank 1 32°16′59.964″ N, 102°24′47.639″ E 3 800 2 32°19′17.561″ N, 102°25′39.714″ E 3 710 3 32°24′17.755″ N, 102°24′29.689″ E 3 599 凸岸 Undercut bank 4 32°17′3.758″ N, 102°24′48.518″ E 3 798 5 32°19′12.308″ N, 102°25′40.332″ E 3 711 6 32°24′14.298″ N, 102°24′30.065″ E 3 601 中游
Middle reaches凹岸 Slip-off bank 7 32°40′24.576″ N, 102°20′25.219″ E 3 510 8 32°47′36.082″ N, 102°27′51.556″ E 3 493 9 32°55′48.497″ N, 102°37′10.249″ E 3 475 凸岸 Undercut bank 10 32°40′35.507″ N, 102°20′15.911″ E 3 510 11 32°47′46.973″ N, 102°27′43.831″ E 3 494 12 32°55′37.160″ N, 102°37′39.990″ E 3 477 下游
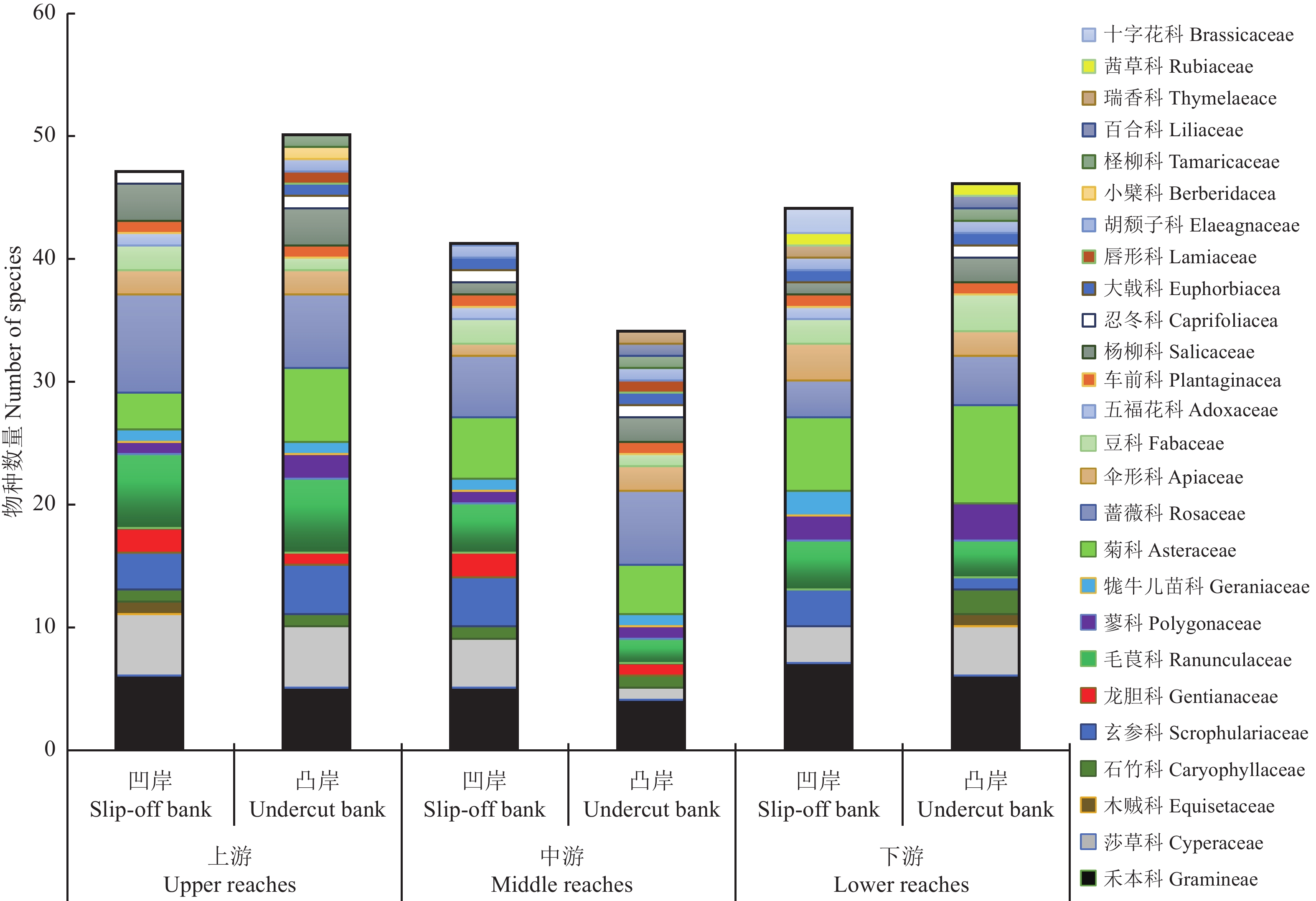
Lower reaches凹岸 Slip-off bank 13 33°11′37.039″ N, 102°34′39.868″ E 3 447 14 33°17′59.492″ N, 102°30′16.453″ E 3 444 15 33°22′25.224″ N, 102°29′7.220″ E 3 436 凸岸 Undercut bank 16 33°11′9.694″ N, 102°34′16.693″ E 3 447 17 33°16′47.729″ N, 102°29′18.209″ E 3 439 18 33°21′4.500″ N, 102°28′36.224″ E 3 437 表 2 白河干流全段岸线植被群落科属种统计
Table 2 Data of families, genera, and species of communities in riparian zones along the channel of the Baihe River
层次
Layer生境类型 Habitat type 科数
Family属数
Genera物种数
Species河段
Studied reaches凹凸岸
Slip-off/undercut bank灌木层
Shrub layer上游
Upper reaches凹岸 Slip-off bank 3 5 7 凸岸 Undercut bank 6 8 10 中游
Middle reaches凹岸 Slip-off bank 4 4 5 凸岸 Undercut bank 5 6 7 下游
Lower reaches凹岸 Slip-off bank 3 3 3 凸岸 Undercut bank 5 5 6 草本层
Herbaceous layer上游
Upper reaches凹岸 Slip-off bank 15 34 40 凸岸 Undercut bank 15 35 40 中游
Middle reaches凹岸 Slip-off bank 16 32 37 凸岸 Undercut bank 16 23 26 下游
Lower reaches凹岸 Slip-off bank 16 35 41 凸岸 Undercut bank 15 31 40 藤本层
Lianaceous layer上游
Upper reaches凹岸 Slip-off bank 凸岸 Undercut bank 中游
Middle reaches凹岸 Slip-off bank 凸岸 Undercut bank 1 1 1 下游
Lower reaches凹岸 Slip-off bank 凸岸 Undercut bank 表 3 白河干流全段岸线植被群落优势种变化
Table 3 Variation in dominant species in riparian zones along the channel of the Baihe River
层次
Layer生境类型 Habitat type 优势种及其重要值
Variation in dominant species and their important value河段
Studied reaches凹凸岸
Slip-off/undercut bank灌木层
Shrub
layer上游
Upper reaches凹岸
Slip-off bank金露梅(22.353 8) + 奇花柳(21.362 7) + 山生柳(13.433 4) Potentilla fruticose (22.353 8) + Salix atopantha (21.362 7) + Salix oritrepha (13.433 4) 凸岸
Undercut bank杯腺柳(28.809 7) + 金露梅(15.527 1) + 奇花柳(15.097 1) Salix cupularis (28.809 7) + Potentilla fruticose (15.527 1) + Salix atopantha (15.097 1) 中游
Middle reaches凹岸
Slip-off bank沙棘(41.639 2) + 奇花柳(39.930 9) + 金露梅(8.432 2) Hippophae rhamnoides (41.639 2) + Salix atopantha (39.930 9) + Potentilla fruticose (8.432 2) 凸岸
Undercut bank奇花柳(35.514 1) + 杯腺柳(15.502 5) + 沙棘(12.937 0) Salix atopantha (35.514 1) + Salix cupularis (15.502 5) + Hippophae rhamnoides (12.937 0) 下游
Lower reaches凹岸
Slip-off bank杯腺柳(42.394 4) + 金露梅(29.961 2) + 沙棘(27.644 4) Salix cupularis (42.394 4) + Potentilla fruticose (29.961 2) + Hippophae rhamnoides (27.644 4) 凸岸
Undercut bank奇花柳(41.311 6) + 杯腺柳(15.529 5) + 沙棘(15.487 1) Salix atopantha (41.311 6) + Salix cupularis (15.529 5) + Hippophae rhamnoides (15.487 1) 草本层
Herbaceous
layer上游
Upper reaches凹岸
Slip-off bank矮生嵩草(12.052 0) + 甘肃嵩草(7.401 7) + 线叶嵩草(6.264 2) Kobresia humilis (12.052 0) + Kobresia kansuensis (7.401 7) + Kobresia capillifolia (6.264 2) 凸岸
Undercut bank甘肃嵩草(12.263 2) + 银叶蕨麻(11.704 8) + 矮生嵩草(6.342 4) Kobresia kansuensis (12.263 2) + Argentina leuconota (11.704 8) + Kobresia humilis (6.342 4) 中游
Middle reaches凹岸
Slip-off bank蕨麻(12.214 6) + 高山藨草(11.758 2) + 矮生嵩草(6.316 2) Argentina anserina (12.214 6) + Scirpus paniculatocorymbosus (11.758 2) + Kobresia humilis (6.316 2) 凸岸
Undercut bank甘肃嵩草(24.021 2) + 珠芽蓼(7.894 3) + 蕨麻(7.043 1) Kobresia kansuensis (24.021 2) + Polygonum viviparum (7.894 3) + Argentina anserina (7.043 1) 下游
Lower reaches凹岸
Slip-off bank甘肃嵩草(12.150 2) + 垂穗披碱草(9.105 0) + 宽叶蒿(7.804 6) Kobresia kansuensis (12.150 2) + Elymus nutans (9.105 0) + Artemisia latifolia (7.804 6) 凸岸
Undercut bank垂穗披碱草(22.707 3) + 蕨麻(7.385 7) + 甘肃嵩草(6.366 6) Elymus nutans (22.707 3) + Argentina anserina (7.385 7) + Kobresia kansuensis (6.366 6) 表 4 白河干流全段草本层物种多样性解释力度
Table 4 Explanatory power of species diversity of herbaceous layer in riparian zones along the channel of the Baihe River
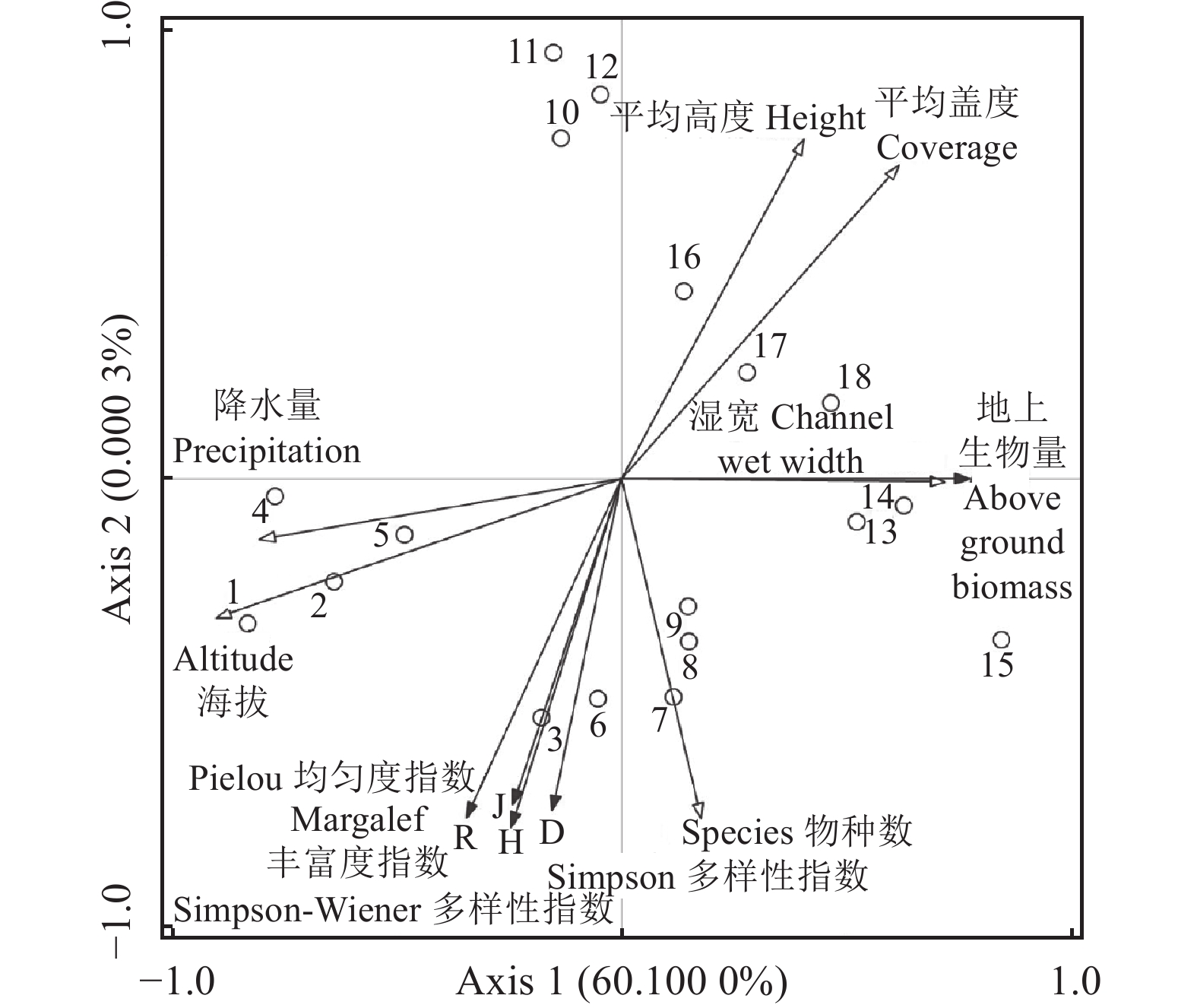
因子
Factor解释力度排序
Rank order of explanatory
variables因子所占解释量 F P Variance explains of factors/% 海拔 Altitude Ⅰ 81.5 15.4 0.004** 物种数 Species Ⅱ 10.2 2.1 0.098* 湿宽 Channel wet width Ⅲ 2.8 0.5 0.484 平均高度 Height Ⅳ 2.8 0.5 0.484 平均盖度 Coverage Ⅴ 2.3 0.4 0.540 降水量 Precipitation Ⅵ 0.4 < 0.1 0.814 *,P < 0.1;**,P < 0.05. 表 5 红原县2019-2021年各乡镇牲畜存栏量
Table 5 Livestock stock in each township of Hongyuan County from 2019 to 2021
头 Head 乡(镇)
Township
(Town)2019 2020 2021 总
Total牛
Cattle马
Horse羊
Sheep总
Total牛
Cattle马
Horse羊
Sheep总
Total牛
Cattle马
Horse羊
Sheep瓦切乡
Wache Township95491 93630 1861 0 85939 84118 1821 0 74277 72642 1635 0 色地镇
Sedi Town87496 84126 3370 0 76293 73614 2679 0 66081 63413 2668 0 安曲镇
Anqu Town85153 77942 2509 4702 75541 68400 2579 4562 65870 59411 2682 3777 麦洼乡
Maiwa Township76727 74448 2279 0 67204 65047 2157 0 58019 55974 2045 0 邛溪镇
Qiongxi Town72485 70318 1227 940 63272 61306 996 970 54566 52702 868 996 查尔玛乡
Chalma Township60679 58612 2087 0 52664 50964 1700 0 45651 43958 1693 0 阿木乡
Amu Township51568 48322 1952 1294 45036 42169 1573 1294 39553 36518 1728 1307 龙日乡
Longri Township50883 48658 1783 442 45698 43647 1508 543 39550 37263 1629 658 江茸乡
Jiangrong Township38757 33142 1966 3649 33336 28155 1532 3649 28235 24378 1080 2777 刷经寺镇
Shujingsi Town35822 32443 3228 151 31140 28297 2712 131 26546 24152 2291 103 -
[1] 韩路, 王海珍, 于军. 河岸带生态学研究进展与展望. 生态环境学报, 2013, 22(5): 879-886. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2013.05.026 HAN L, WANG H Z, YU J. Research progress and prospects on riparian zone ecology. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2013, 22(5): 879-886. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2013.05.026
[2] 周铭浩, 邱静, 洪昌红, 杜欢欢, 汤海平. 河岸带功能及其保护修复措施. 黄河水利职业技术学院学报, 2019, 31(4): 6-11. doi: 10.13681/j.cnki.cn41-1282/tv.2019.04.002 ZHOU M H, QIU J, HONG C H, DU H H, TANG H P. Riparian zone function and its protection and remediation measures. Journal of Yellow River Conservancy Technical Institute, 2019, 31(4): 6-11. doi: 10.13681/j.cnki.cn41-1282/tv.2019.04.002
[3] 余飞燕, 王坤悦, 叶鑫, 董洪君, 黄凯, 罗志力, 郝建锋. 金马河温江段河岸带不同生境草本群落物种多样性和生物量变化研究. 草地学报, 2020, 28(3): 793-800. YU F Y, WANG K Y, YE X, DONG H J, HUANG K, LUO Z L, HAO J F. Research on species diversity and biomass variation of herbaceous communityin difference habitats in Wenjiang Section of Jinma River. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2020, 28(3): 793-800.
[4] 曾艳. 不同土地利用类型下河岸带草本植物群落结构及其影响因素. 南京: 南京大学硕士学位论文, 2015. ZENG Y. The effects of land use on herbaceouscommunity structure in the riparian zone. Master Thesis. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2015
[5] 张建春, 彭补拙. 河岸带及其生态重建研究. 地理研究, 2002(3): 373-383. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2002.03.013 ZHANG J C, PENG B Z. Research on riparian zone and its ecological reconstruction. Geographical Studies, 2002(3): 373-383. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0585.2002.03.013
[6] 邓红兵, 王青春, 王庆礼, 吴文春, 邵国凡. 河岸植被缓冲带与河岸带管理. 应用生态学报, 2001(6): 951-954. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2001.06.035 DENG H B, WANG Q C, WANG Q L, WU W C, SHAO G F. Riparian vegetation buffer zone and riparian zone management. Journal of Applied Ecology, 2001(6): 951-954. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9332.2001.06.035
[7] CHANG T P, TOEBES G H. A statistical comparison of meander planforms in the Wabash Basin. Water Resources Research, 1970, 6(2): 557-578.
[8] SWAMEE P K, PARKASH B, THOMAS J V, SINGH S. Changes in channel pattern of river ganga between mustafabad and rajmahal, gangetic plains since 18th century. International Journal of Sediment Research, 2003, 13(3): 219-231.
[9] 刘成, 刘桉, 徐梦珍. 白河河湾迁移速率及影响因素分析. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 2018, 16(5): 495-502, 509. doi: 10.13244/j.cnki.jiwhr.2018.05.020 LIU C, LIU A, XU M Z. Analysis on migration rate and influencing factors of Baihe Bay. Journal of China Academy of Water Resources and Hydropower Sciences, 2018, 16(5): 495-502, 509. doi: 10.13244/j.cnki.jiwhr.2018.05.020
[10] 杜际增, 王根绪, 李元寿. 近45年长江黄河源区高寒草地退化特征及成因分析. 草业学报, 2015, 24(6): 5-15. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2014302 DU J Z, WANG G X, LI Y S. Degradation characteristics and causes of alpine grasslands in the source region of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers in recent 45 years. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2015, 24(6): 5-15. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2014302
[11] 薛娴, 郭坚, 张芳, 宗莉, 韩邦帅, 黄翠华. 高寒草甸地区沙漠化发展过程及成因分析: 以黄河源区玛多县为例. 中国沙漠, 2007(5): 725-732. XUE X, GUO J, ZHANG F, ZONG L, HAN B S, HUANG C H. Development and cause of aeolian desertification in Alpine Region: In case of Maduo County in Yellow River Source Area. Journal of Desert Research, 2007(5): 725-732.
[12] KAWAI S, JULIEN P Y. Point bar deposits in narrow sharp bends. Journal of Hydraulic Research, 1996, 34(2): 205-218. doi: 10.1080/00221689609498497
[13] 杨玥, 李志威, 胡旭跃, 吴新宇. 黄河源白河与黑河下游凸岸点边滩形态与变化规律. 泥沙研究, 2021, 46(1): 50-56, 17. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2021.01.007 YANG Y, LI Z W, HU X Y, WU X Y. Morphological characteristics and processes of point bars in the lower White and Black Rivers of the Yellow River Source region. Journal of Sediment Research, 2021, 46(1): 50-56, 17. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2021.01.007
[14] CZORTEK P, DYDERSKI M K, JAGODZINSKI A M. River regulation drives shifts in urban riparian vegetation over three decades. Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, 2019, 47: 126542.
[15] 曲晓涵, 王雪岩. 大连市河岸带生态恢复与植被重建研究. 科技经济导刊, 2019, 27(20): 113. QU X H, WANG X Y. Research on ecological restoration and vegetation reconstruction of Riparian Zone in Dalian City. Technology and Economic Guide, 2019, 27(20): 113.
[16] 胡彬, 翟文静, 赵警卫. 河岸带植被对河流生态功能影响研究进展. 福建林业科技, 2015, 42(3): 233-239. HU B, ZHAI W J, ZHAO J W. Progresses in researches on the influence of riparian vegetation on river ecological functions. Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology, 2015, 42(3): 233-239.
[17] 武晓倩, 范保硕, 滕叶文, 李荣琦, 渠开跃, 钱金平, 田冰. 白洋淀流域河岸带草本植物群落分布特征与土壤环境因子的关系. 应用与环境生物学报, 2022, 28(6): 1608-1614. doi: 10.19675/j.cnki.1006-687x.2021.05043 WU X Q, FAN B S, TENG Y W, LI R Q, QU K Y, QIAN J P, TIAN B. Relationship between herbaceous community distribution and soil environmental factors in riparian zone of Baiyangdian River Basin. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2022, 28(6): 1608-1614. doi: 10.19675/j.cnki.1006-687x.2021.05043
[18] 杨树青, 白玉川, 徐海珏, 黄哲. 河岸植被覆盖影响下的河流演化动力特性分析. 水利学报, 2018, 49(8): 995-1006. YANG S Q, BAI Y C, XU H Y, HUANG Z. Dynamic characteristics of river evolution under the influence of riparian vegetation cover. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2018, 49(8): 995-1006.
[19] 朱海丽, 胡夏嵩, 李志威, 刘亚斌. 黄河源区弯曲河道草甸型植被分布特征. 泥沙研究, 2018, 43(1): 58-65. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2018.01.010 ZHU H L, HU X S, LI Z W, LIU Y B. Zoning characteristics and processes in convex bank of meander reaches with riparian meadow in source region of the Yellow River. Journal of Sediment Research, 2018, 43(1): 58-65. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2018.01.010
[20] 刘桉. 黄河源区典型弯曲河流演变与滨河植被的作用研究. 北京: 中国水利水电科学研究院硕士学位论文, 2018. LIU A. Relation between riparian vegetation and meander migration for typical meaning rivers in the Yellow River source region. Master Thesis. Beijing: China Academy of Water Resources and Hydropower Sciences, 2018.
[21] 赵资乐. 黄河上游黑河、白河流域水沙规律. 甘肃水利水电技术, 2005(4): 336-338, 350. ZHAO Z L. The regularity of water and sediment in the Heihe and Baihe river basins in the upper reaches of the Yellow River. Gansu Water Resources and Hydropower Technology, 2005(4): 336-338, 350.
[22] 李志威, 王兆印, 李艳富, 刘乐. 黄河源区典型弯曲河流的几何形态特征. 泥沙研究, 2012(4): 11-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0468-155X.2012.04.003 LI Z W, WANG Z Y, LI Y F, LIU L. Geometric characteristics of typical curved rivers in the source region of the Yellow River. Journal of Sediment Research, 2012(4): 11-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0468-155X.2012.04.003
[23] 方精云, 王襄平, 沈泽昊, 唐志尧, 贺金生, 于丹, 江源, 王志恒, 郑成洋, 朱江玲, 郭兆迪. 植物群落清查的主要内容、方法和技术规范. 生物多样性, 2009, 17(6): 533-548. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09253 FANG J Y, WANG X P, SHEN Z H, TANG Z Y, HE J S, YU D, JIANG Y, WANG Z H, ZHENG C Y, ZHU J L, GUO Z D. Main contents, methods and technical specifications of plant community inventory. Biodiversity Science, 2009, 17(6): 533-548. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1003.2009.09253
[24] LIN T, DONG S, SHERMAN R, LIU S, WU X. Changes in vegetation composition and plant diversity with rangeland degradation in the alpine region of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. The Rangeland Journal, 2015, 37(1): 107-115. doi: 10.1071/RJ14077
[25] 张帆, 李元淳, 王新, 朱剑霄. 青藏高原高寒草甸退化对草地群落生物量及其分配的影响. 草业科学, 2021, 38(8): 1451-1458. doi: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2020-0710 ZHANG F, LI Y C, WANG X, ZHU J X. Effect of rangeland degradation on biomass allocation in alpine meadows on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Pratacultural Science, 2021, 38(8): 1451-1458. doi: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2020-0710
[26] 李成阳, 张文娟, 赖炽敏, 彭飞, 陈小杰, 薛娴, 王涛, 尤全刚, 杜鹤强. 黄河源区不同退化程度高寒草原群落生产力、物种多样性和土壤特性及其关系研究. 生态学报, 2021, 41(11): 4541-4551. LI C Y, ZHANG W J, LAI C M, PENG F, CHEN X J, XUE X, WANG T, YOU Q G, DU H Q. Plant productivity, species diversity, soil properties, and their relationships in an alpine steppe under different degradation degrees at the source of the Yellow River. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(11): 4541-4551.
[27] 陈影, 陈苏, 马鸿岳, 单岳, 冯天朕, 张鸿龄. 辽河干流河岸带植物及微生物多样性研究. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(9): 2048-2057. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0311 CHEN Y, CHEN S, MA H Y, SHAN Y, FENG T Z, ZHANG H L. Plant and microbial diversity in the riparian zone of the Liao River mainstream, China. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2020, 39(9): 2048-2057. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2020-0311
[28] 富金赤, 李晓莎, 许中旗, 郭延朋, 赵娱, 李校. 冀北山地阳坡草本植物物种多样性的空间异质性研究. 草地学报, 2018, 26(6): 1298-1304. FU J C, LI X S, XU Z Q, GUO Y P, ZHAO Y, LI X. Spatial heterogeneity of herbaceous plant species diversity in dry south-slope of North Mountain of Hebei. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2018, 26(6): 1298-1304.
[29] 何松. 嘉陵江中下游河岸植被及植物多样性研究. 重庆: 西南大学硕士学位论文, 2019. HE S. Research on riparian vegetation and plant diversity in the middle and lower reaches of Jialing River. Master Thesis. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2019.
[30] 孔庆仙, 信忠保, 夏晓平. 北京怀九河河岸带植物多样性及影响因子分析. 科技导报, 2017, 35(24): 57-65. KONG Q X, XIN Z B, XIA X P. Analysis of plant diversity and influencing factors in the riparian zone of Huaijiu River in Beijing. Science & Technology Review, 2017, 35(24): 57-65.
[31] 汪殿蓓, 暨淑仪, 陈飞鹏. 植物群落物种多样性研究综述. 生态学杂志, 2001, 20(4): 55-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2001.04.015 WANG D B, JI S Y, CHEN F P. A review of studies on plant community species diversity. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2001, 20(4): 55-60. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4890.2001.04.015
[32] WANG C T, LONG R J, WANG Q L, JING Z C, SHI J J. Changes in plant diversity, biomass and soil C, in alpine meadows at different degradation stages in the headwater region of three rivers, China. Land Degradation & Development, 2009, 20(2): 187-198.
[33] LI C Y, PENG F, XUE X, YOU Q G, LAI C M, ZHANG W J, CHENG Y X. Productivity and quality of alpine grassland vary with soil water availability under experimental warming. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 1790.
[34] 李成阳, 赖炽敏, 彭飞, 薛娴, 尤全刚, 张文娟, 刘斐耀. 青藏高原北麓河流域不同退化程度高寒草甸生产力和群落结构特征. 草业科学, 2019, 36(4): 1044-1052. LI C Y, LAI C M, PENG F, XUE X, YOU Q G, ZHANG W J, LIU F Y. Alpine meadows at different stages of degradation in the Beiluhe Basin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Productivity and community structure characteristics. Pratacultural Science, 2019, 36(4): 1044-1052.
[35] 朱海丽, 王兆印, 李志威. 黄河源区滨河草甸对弯曲河流河道演变的影响. 人民黄河, 2013, 35(4): 41-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2013.04.015 ZHU H L, WANG Z Y, LI Z W. Influence of riparian meadow to the Meandering Rivers evolution in the Yellow River Source Region. Yellow River, 2013, 35(4): 41-44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2013.04.015
[36] 谢彬山, 朱海丽, 李本锋, 胡夏嵩. 黄河源区曲流滨河植被空间分布与土壤特性关系研究. 泥沙研究, 2019, 44(6): 66-73. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2019.06.011 XIE B S, ZHU H L, LI B F, HU X S. Study on relationship between vegetation spatial distribution and soil properties in the meander riverside in source region of the Yellow River. Journal of Sediment Research, 2019, 44(6): 66-73. doi: 10.16239/j.cnki.0468-155x.2019.06.011
[37] 朱海丽. 黄河源区弯曲河流滨河植被增强河岸稳定作用机理研究. 西宁: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院青海盐湖研究所)博士学位论文, 2018. ZHU H L. Study on the mechanism of riverbank stabilization reinforcement by the riparian vegetation of meandering river in the Yellow River source region. PhD Thesis. Xining: Chinese Academy of Sciences (Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2018
[38] 王丹阳. 青藏高原弯曲河流地貌单元对有机碳迁移的影响规律和机制. 长沙: 湖南大学博士学位论文, 2020. WANG D Y. Pattern and mechanism of influence of geomorphic units within meandering river of the Tibetan Plateau on organic carbon transport. PhD Thesis. Changsha: Hunan University, 2020.
[39] 张文丽, 夏会娟, 张远, 孔维静, 贾晓波, 姚懿函. 东辽河河岸带草本植物物种多样性及群落数量分析. 生态学杂志, 2014, 33(5): 1142-1149. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.2014.0121 ZHANG W L, XIA H J, ZHANG Y, KONG W J, JIA X B, YAO Y H. Herbaceous species diversity and community quantitative analysis in the riparian zone of East Liaohe River. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2014, 33(5): 1142-1149. doi: 10.13292/j.1000-4890.2014.0121
[40] 陈吉泉. 河岸植被特征及其在生态系统和景观中的作用. 应用生态学报, 1996, 7(4): 439-448. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.1996.0086 CHEN J Q. Riparian vegetation characteristics and their functions in ecosystems and landscapes. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 1996, 7(4): 439-448. doi: 10.13287/j.1001-9332.1996.0086
[41] 李良涛. 农田边界和居民庭院植物多样性分布格局及植被营建. 北京: 中国农业大学博士学位论文, 2014. LI L T. Distribution pattern of plant diversity and vegeta-tion construction in field margins and homegarden. PhD Thesis. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2014.



 下载:
下载: